Hyperautomation, a term coined by Gartner in 2019, is defined as “a business-driven, disciplined approach that organizations use to rapidly identify, vet and automate as many business and IT processes as possible.” Even Gartner has deviated from this definition recently with the introduction of Business Orchestration Automation Technologies (BOAT) at the Gartner AIBS Summit in May of 2024, which adds a layer of orchestration on top of automation technologies.
Some of the in-market incumbent RPA vendors are attempting to perform a pivot to Agentic Process Automation (APA) to signal that they have fully embraced Agentic AI adaptability and speed, but in doing so, they present several new challenges on the way to hyperautomation.
As Gartner intended it, hyperautomation occurs upon successful implementation of multiple technology solutions—AI, LLMs, RPA, IDP, BPM, iPaaS, and more—to automate as much as possible. But this acronym soup leaves a bad taste due to its fragility, high costs, and maintenance challenges. Rather than using disparate solutions to accomplish full-scale enterprise automation, companies turned back to their incumbent automation solutions and tried to overlook its faults.
Despite the fact that vendors abused the term as a buzzword instead of seeing its full potential (see: agentic AI in the 2024 automation market), hyperautomation is possible.
Unrealized Expectations of Hyperautomation
Conceptually, hyperautomation promised to revolutionize business processes by enabling end-to-end automation. In practice, however, moving beyond the concept proved challenging for several reasons:
- Complexity and Integration Challenges: Hyperautomation has always required integrating complex and costly technologies, making it difficult for organizations to realize a positive ROI in a timely manner.
- Overpromising by Vendors: As we noted above, when hyperautomation hit the market, vendors used it heavily in their marketing, but the product didn’t live up to expectations when customers started using it.
- Limited Adoption: For organizations who actually moved beyond consideration and attempted to implement hyperautomation, the task often became insurmountable as a result of both cost and complexity.
Misuse of Hyperautomation in RPA and IDP
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) have both been mislabeled as hyperautomation solutions, rather than components of a larger hyperautomation strategy. While both technologies contribute to hyperautomation as the market currently knows it, along with many other technologies like AI and iPaaS, they are not hyperautomation in and of themselves.
RPA excels at automating repetitive, predictable tasks, but it lacks cognitive capabilities to solve complex processes that require human-like decision-making ability.
IDP is great at processing unstructured data from documents, but is limited in terms of use cases it can serve and frequently fails to integrate with larger enterprise systems.
Neither of these solutions constitutes hyperautomation, though both could contribute to a hyperautomation strategy alongside other technologies.
Practical Implementation of Hyperautomation
In order to stay competitive, anything that can be automated, must be automated. Kognitos brings the original vision of hyperautomation to life by automating virtually any IT or business process you can dream up, all with a serverless infrastructure that maintains a system of record accessible to any business stakeholder who can read in plain English.
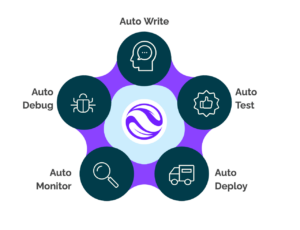
Our Hyperautomation Lifecycle (HAL) platform doesn’t require integrating multiple automation technologies, because we’ve done that work for you on the front end. HAL can automate the entire lifecycle of creating automations, truly bringing hyperautomation to life, without the cost and headaches outlined in the original Gartner definition. For the first time, end-to-end business process automation is possible with one solution. Here’s how it works:
- Auto Write: Provide simple instructions and automatically create sophisticated workflows, eliminating the need for complex coding or technical expertise. If you have an SOP, you can now deploy a process automation.
- Auto Test: Verify the functionality and reliability of your automated workflows without manual intervention. The system simulates various scenarios and edge cases, ensuring that the automation performs as expected across different conditions.
- Auto Deploy: Kognitos’ HAL relies on an invisible, serverless infrastructure to ensure rapid and reliable releases. Minimize human error, enhance consistency, and accelerate speed throughout your entire automation lifecycle.
- Auto Monitor: Continuously observe and assess the performance, health, and security of every automation, with an accessible system of record in natural language. The system will note any exceptions and pause to ask for human guidance, if needed, instead of breaking.
- Auto Debug: For any issues that arise during Auto Monitoring, Kognitos will apply its own bug fixes and confirm with a human team member as needed.
If you’re interested in learning more about how your organization can simply automate more, reach out to a member of our team for a customized demonstration of how HAL can work for you.

Discover the Power of Kognitos
Our clients achieved:
- 75%manual data entry eliminated
- 30 hourssaved on invoicing per week
- 2 millionreceipts analyzed per year